Q.1 An Alternating quantity which change its ___.
A. direction only
B. magnitude only
C. direction and magnitude
D. none of the above
Ans.: C
Q.02 An alternating current or voltage is any current that varies in both magnitude and direction with respect to___.
A. speed
B. velocity
C. acceleration
D. time
Ans.: D
Q.03 The ____ of voltage or ______ of current occurs at regular intervals of time.
A. reversal of polarity, reversal of polarity
B. reversal of polarity, direction
C. Direction, reversal of polarity
D. direction, direction
Ans.: B
Q.04 A circuit in which alternating currents flow are called___.
A. alternating voltage circuit
B. alternating current circuits
C. alternating circuit
D. all of the above
Ans.: B
Q.05 what are the advantages of AC over DC?
A. can be easily generated
B. can be easily transmitted
C. can be easily utilized
D. all of the above
Ans.: D
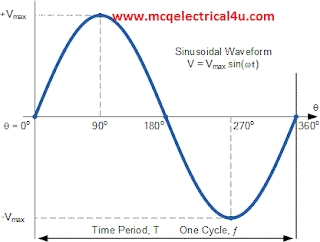
Q.06 The shape of the curve obtained by plotting the value voltage or current at different instant on vertical axis and time or angle on horizontal axis is called___
A. wave shape
B. waveform
C. Both A or B
D. alternating quantity
Ans.: C
Q.07 Alternating quantity may have__.
A. rectangular shave
B. square shape
C. triangular shape
D. any shape
Ans.: D
Q.08 which of the following wave is basic of all alternating voltage or currents?
A. square wave
B. sine wave
C. cosine wave
D. rectangular wave
Ans.: B
Q.09 The quantity which obeying sine law are called___
A. sinusoids
B. sinusoidal quantities
C. cosine quantity
D. Both A or B
Ans.: D
Q.10 It is necessary for the waveform above the horizontal axis to have same shape as that below axis?
A. not necessary
B. necessary
C. may be
D. none f the above
Ans.: A
Q.11 In an alternating quantity, the wave is symmetrical about the ____.
A. vertical axis
B. horizontal axis
C. half portion is on vertical and remaining is on horizontal axis
D. none of the above
Ans.: B
Q.12 One complete alternation or repetition of a set of values of current is called___.
A. frequency
B. angular speed
C. cycle
D. rotation
Ans.: C
Q.13 Each complete cycle consists of the positive half cycle ____, and the negative half cycle _____.
A. below the horizontal axis, above the vertical axis
B. below the horizontal axis, below the vertical axis
C. above the horizontal axis, above the vertical axis
D. above the horizontal axis, below the horizontal axis
Ans.: D
Q.14 what is frequency?
A. no. of cycle completed in one second
B. no. of cycle completed in one minutes
C. no. of cycle completed in one hour
D. no. of cycle completed in one millisecond
Ans.: A
Q.15 Which of the following is/are correct for frequency?
A. Unit of frequency is Hz
B. In power systems frequency of 50 Hz and 60 Hz are used
C. in communication system frequencies up to millions of hertz are used
D. All of the above
Ans.: D